The current paradigm of undergraduate medical education places a strong emphasis on the cultivation of competencies and measurable outcomes, particularly through the development of essential skills at every stage of learning. This approach delineates competencies such as 'Shows How' (SH) or 'Perform' (P), which are intricately linked to the acquisition of specific skills by the learner. With the Graduate Medical Education Regulations Part II, 2019 outlining certain skills as prerequisites for graduation, institutions are tasked with the responsibility of facilitating skill sessions tailored to the acquisition of essential or desirable competencies, while ensuring proper documentation of this process.
To meet these requirements effectively, institutions often establish skills labs, providing a controlled and safe environment conducive to skill acquisition. Within these labs, learners can engage in hands-on training, closely observed and provided with constructive feedback to aid improvement. This iterative process allows learners to repetitively practice tasks under supervision until the desired level of competency is attained.
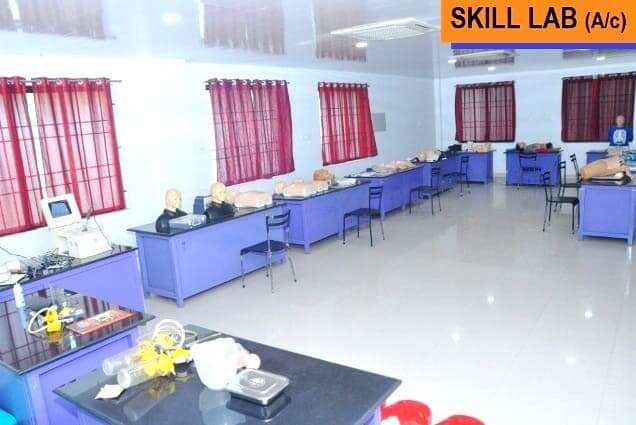
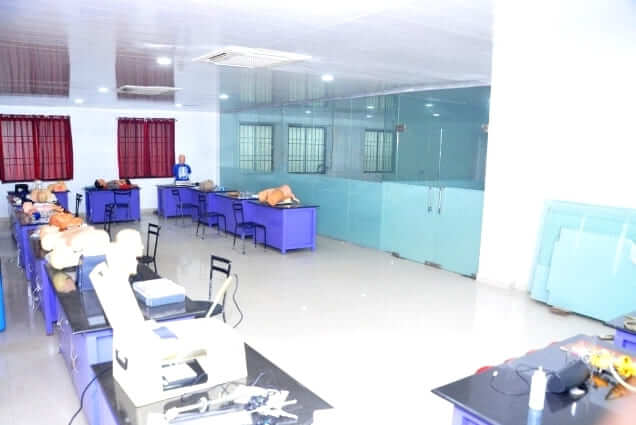
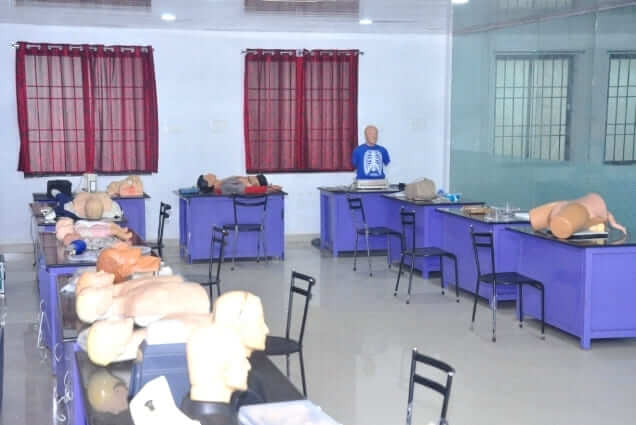
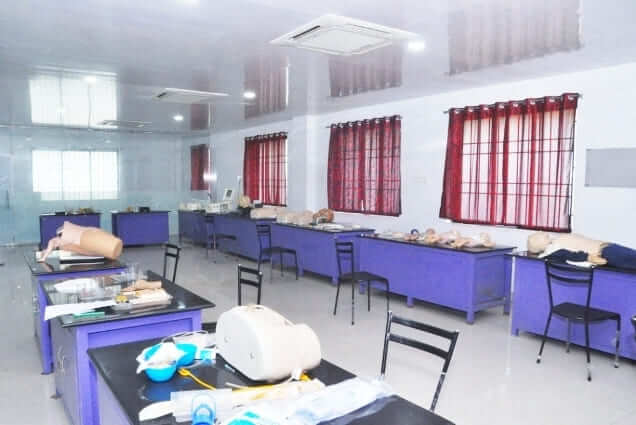






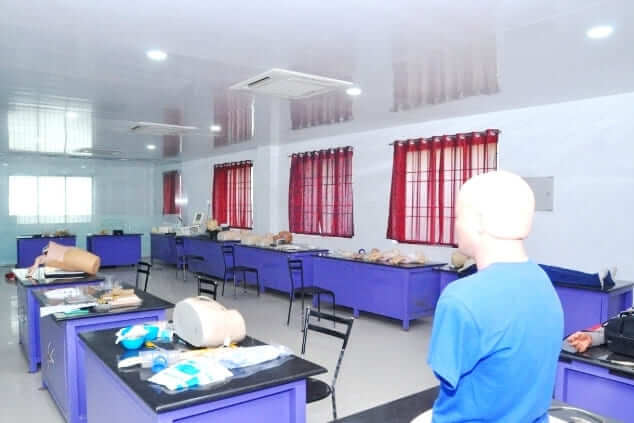

The importance of skill training extends beyond mere procedural knowledge. It serves as a bridge between competency and skill, enabling students to understand the underlying principles of skill acquisition and their practical application. Through structured training sessions, students not only learn the specific methods and steps involved in skill acquisition but also grasp the broader skill cycle, encompassing various stages of learning and mastery.
Integral to this approach is the active involvement of students in procedure patient care skills training, which fosters experiential learning under supervision. Additionally, the integration of life support skills training from the outset of the curriculum ensures that students are equipped with essential lifesaving abilities, with training progressing from basic to advanced levels by the culmination of their internship.
In essence, skill training within the medical education framework serves as a cornerstone for competency development, providing students with the necessary tools to navigate clinical practice effectively and ethically. By prioritizing hands-on learning, guided practice, and continuous feedback, institutions can empower future healthcare professionals to deliver optimal patient care and contribute meaningfully to the healthcare ecosystem.
ALL RIGHT RESERVED | VMMCKKL.EDU.IN KARAIKAL